Abstract
Background and purpose
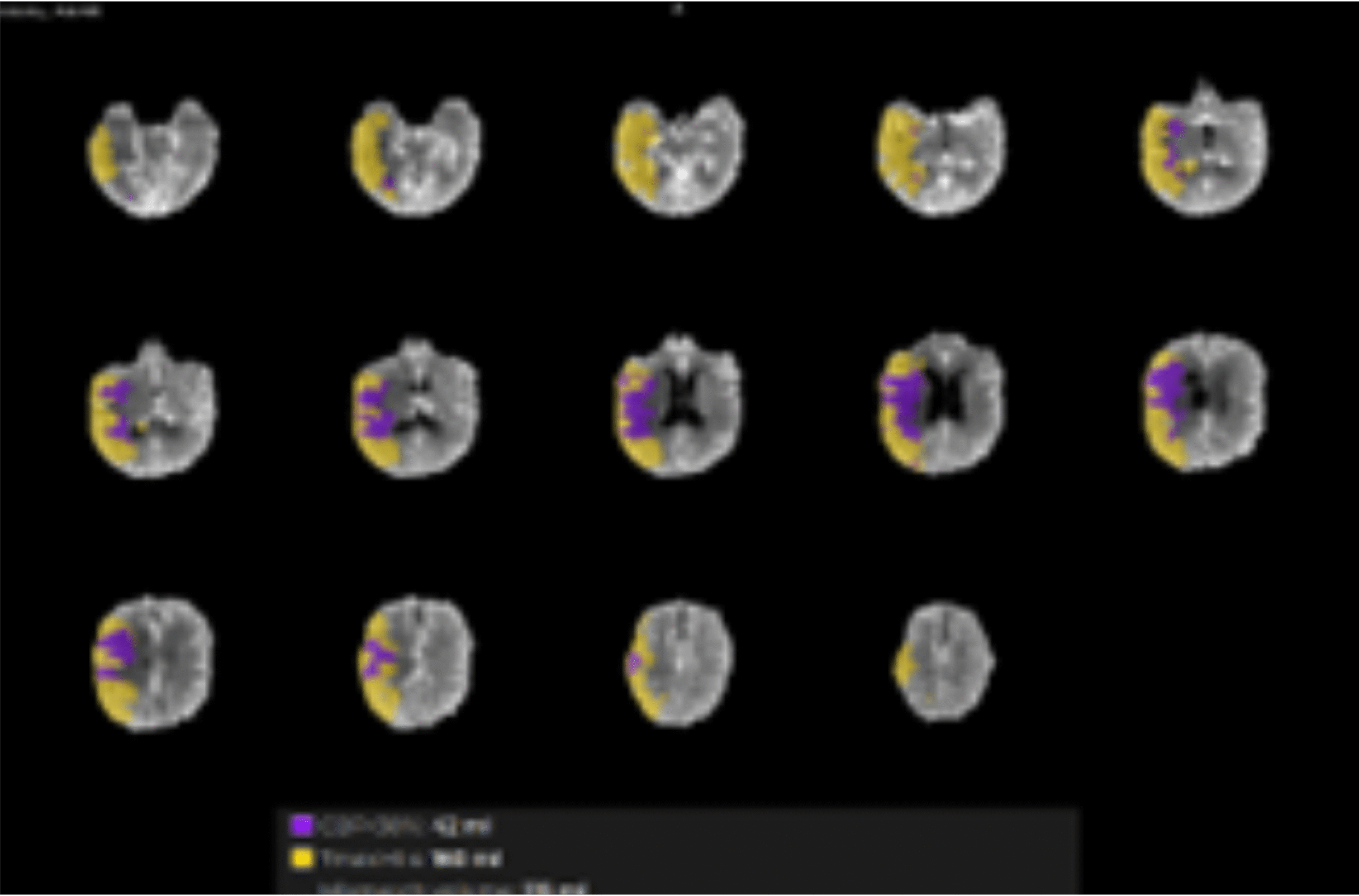
Treatment options for patients with acute ischemic stroke depend on the volume of salvageable tissue. This volume assessment is currently based on fixed thresholds and single imagine modalities, limiting accuracy. We wish to develop and validate a predictive model capable of automatically identifying and combining acute imaging features to accurately predict final lesion volume using deep convolutional neural networks.
Conclusion
The considerable prediction improvement accuracy over the current state of the art increases the potential for automated decision support in providing recommendations for personalized treatment plans.
Get access to the full article doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019740