Abstract
Objectives
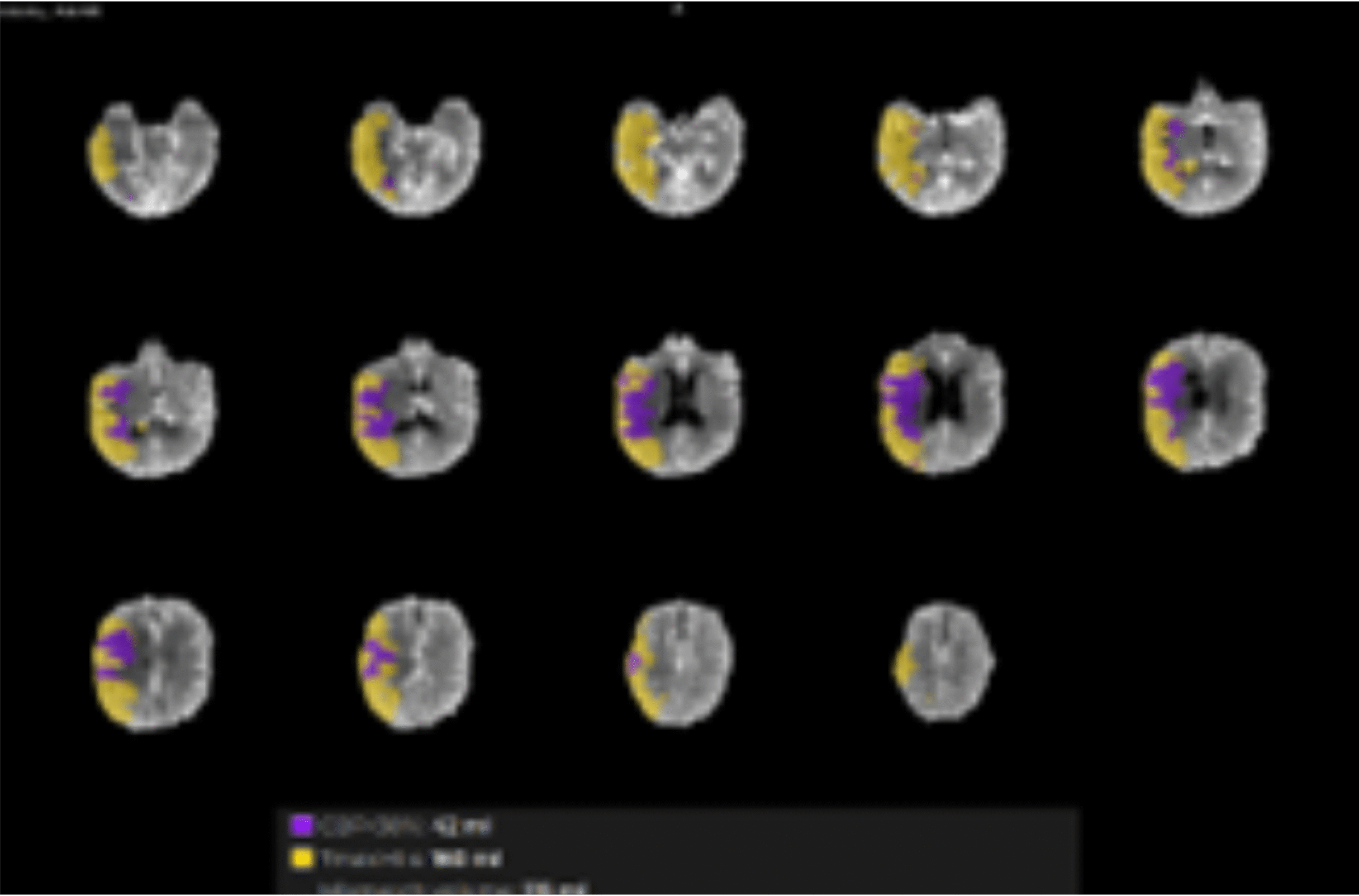
Lesion detection in acute stroke by computed-tomography perfusion (CTP) can be affected by incomplete bolus coverage in veins and hypoperfused tissue, so-called bolus truncation (BT), and low contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). We examined the BT-frequency and hypothesized that image down-sampling and a vascular model (VM) for perfusion calculation would improve normo- and hypoperfused tissue classification.
Conclusion
BT is not uncommon in stroke CTP with 40-s scan duration. Applying image down-sampling and VM improve tissue classification.
Get access to the full article: doi:10.1007/s00330-015-3602-x